Indigenous Technical Knowledge For ODF
Back

Organic Dairy farming means raising animals on organic feed (i.e. pastures cultivated without the use of fertilizers or pesticides), have access to pasture or outside, along with the restricted usage of antibiotics and hormones. Products obtained from Organic dairy farm are the organic dairy products. Organic farming is a system of production, a set of goal-based regulations that allow farmers to manage their own particular situations individually, while maintaining organic integrity. In the organic dairy farms following protocols/standards are followed.
• Cows and calves are fed 100% organic feed.
• Organic crops, hay, and pasture are grown without the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides that have not been carefully screened and approved for organic use.
• Non-natural feed additives and supplements such as vitamins and minerals must also be approved for use in organic.
• Genetically modified organisms (GMOs, called “Excluded Methods” in the regulation) are strictly forbidden.
• Land used to grow organic crops must be free of all prohibited materials for at least three years prior to the first organic harvest.
• Synthetic milk replacers are prohibited. Calves must be fed organic milk.
• All animals must have access to the outdoors, weather permitting. Animals over six months of age must have access to pasture during the growing season.
• Only approved health care products can be used. Many of these are restricted in how and when they can be used. Antibiotics are not allowed.
• Organic animals may not be fed ANY slaughter by-products, urea, or manure.
• The welfare of the animals must be attended to. Certain procedures, such as tail docking, are prohibited. Other procedures, such as dehorning, must be done so as to minimize the stress to the animal.
• An organic farmer must keep sufficient records to verify his or her compliance with the standards.
• Each farm is inspected and audited every year. Any farm can be inspected unannounced at any time.
In order to achieve these above mentioned protocols our ethno veterinary knowledge or indigenous traditional knowledge are of great help.
Indian traditional knowledge or ITKs for organic agricultureIntroduction
• Indigenous Technical Knowledge (ITK) is the actual knowledge of a given population that reflects the experiences based on tradition and includes more recent experiences with modern technologies.
• Indigenous agricultural practices (IAPs) are an unwritten body of knowledge. There is no systematic record to describe what they are, what they do and how they do what they do, how they can be changed, their operations, their boundaries and their applications. It is held in different brains, languages and skills in as many groups, cultures and environments as are available today.
• Indigenous Technical Knowledge is the local knowledge, a knowledge that is unique to a given culture or society. It contrasts with the international knowledge system generated by universities, research institutions and private firms. It is the basis for local–level decision making in agriculture, health care, food preparation, education natural resource management and a host of other activities in rural communities.
• Indian farmers, over centuries have learnt to grow food and to survive in difficult environments; where rich tradition of ITK has been interwoven with the agricultural practices followed by them.
Some of the famous ITKs developed by progressive organic farmers of India are provided hereunder
Ingredients
• Cow Dung- 5kg
• Cow urine- 5L
• Cow milk- 1L
• Lime- 250g
• Water- 100L

Method of Use:
Scientifically Validated by: TNAU, Coimbatore and CSKHPKV, Palampur.
Sanjivak
Ingredients
• Cow urine-100L
• Cow dung-100-200kg
• Jaggery-500g
• Water-300L
Kept for 10 days to ferment
Method of Application
What is Panchagavya?
Panchagavya is an organic product having the potential to play the role of promoting growth and providing immunity in plant system. Panchagavya consists of nine products viz. cow dung, cow urine, milk, curd, jaggery, ghee, banana, Tender coconut and water. When suitably mixed and used, these have miraculous effects.
How to prepare Panchagavya?
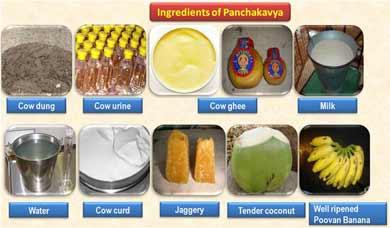
• Cow dung - 7 kg
• Cow ghee - 1 kg
Mix the above two ingredients thoroughly both in morning and evening hours and keep it for 3 days
• Cow Urine - 10 liters
• Water - 10 liters
After 3 days mix cow urine and water and keep it for 15 days with regular mixing both in morning and evening hours. After 15 days mix the following and panchagavya will be ready after 30 days.
• Cow milk - 3 liters
• Cow curd - 2 liters
• Tender coconut water - 3 liters
• Jaggery - 3 kg
• Well ripened poovan banana – 12 nos.
All the above items can be added to a wide mouthed mud pot, concrete tank or plastic can as per the above order. The container should be kept open under shade. The content is to be stirred twice a day both in morning and evening. The Panchagavya stock solution will be ready after 30 days. (Care should be taken not to mix buffalo products. The products of local breeds of cow is said to have potency than exotic breeds). It should be kept in the shade and covered with a wire mesh or plastic mosquito net to prevent houseflies from laying eggs and the formation of maggots in the solution. If sugarcane juice is not available add 500 g of jaggery dissolved in 3 liter of water.
Recommended dosage
Spray system: 3% solution was found to be most effective compared to the higher and lower concentrations investigated. Three litres of Panchagavya to every 100 litre of water is ideal for all crops. The power sprayers of 10 litre capacity may need 300 ml/tank. When sprayed with power sprayer, sediments are to be filtered and when sprayed with hand operated sprayers, the nozzle with higher pore size has to be used.
Flow system : The solution of Panchagavya can be mixed with irrigation water at 50 litre per hectare either through drip irrigation or flow irrigation
Seed/seedling treatment: 3% solution of Panchagavya can be used to soak the seeds or dip the seedlings before planting. Soaking for 20 minutes is sufficient. Rhizomes of Turmeric, Ginger and sets of Sugarcane can be soaked for 30 minutes before planting.
Seed storage: 3% of Panchagavya solution can be used to dip the seeds before drying and storing them.
Seed storage: 3% of Panchagavya solution can be used to dip the seeds before drying and storing them.

Ethno-veterinary Formulations for Important Ailments in Bovines
Mastitis (all types)
Ingredients:
a) Aloe vera – 250 g; b) Turmeric- 50 g (rhizome or powder); c) Calcium Hydroxide (lime)-15 g; d) Lemon – 2 nos.
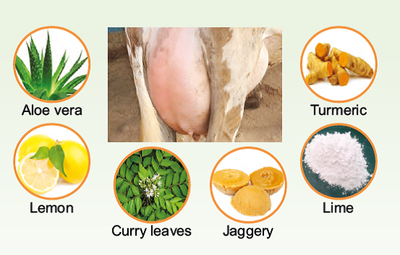
Preparation:
1. Blend ingredients (a to c only) to form a reddish paste.
2. Cut both lemons into half.
Application:
1. Make a handful of paste watery by adding 150- 200 ml of water.
2. Wash and clean the udder and apply the mixture throughout.
3. Repeat application 10 times a day for 5 days.
4. Feed 2 lemons twice daily for 3 days.
Note : For blood in milk, in addition to the above, make a paste of curry leaves (2 handfuls) and jaggery and feed orally twice daily till condition resolves.
Teat obstruction
Ingredients:
Freshly plucked & clean neem leafstalk– 1; Turmeric powder; Butter or Ghee
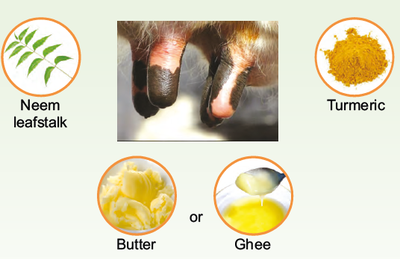
Preparation:
Preparation:
1. Nip the neem leafstalk at the required length based on teat length.
2. Coat the turmeric powder & butter/ghee mixture thoroughly on the neem leafstalk.
Application:
1. Insert the coated neem leafstalk into the affected teat in an anti-clockwise direction.
2. Replace with fresh neemstalk after each milking.
Udder Oedema
Ingredients:
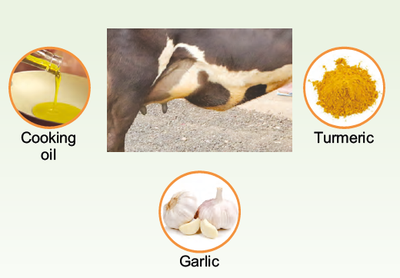 Preparation:
Preparation:
1. Heat oil, add turmeric powder and sliced garlic.
2. Mix well and remove from flame just as the favour develops (no need to boil).
3. Allow to cool.
Application:
1. Apply in a circular manner with force over the entire oedematous region and udder.
2. Apply 4 times a day for 3 days.
Note : Rule out mastitis before using the formulation.
Retention of Placenta
Ingredients:
White radish – 1 full tuber; Lady’s finger - 1.5 kg; Jaggery- as required; Salt- as required
 Preparation:
Preparation:
(i) Cut each lady’s finger into 2 pieces.
Application:
1. Feed one full tuber radish within two hours of calving.
2. Feed 1.5 Kg of fresh lady’s finger with jaggery and salt if ROP persists after 8 hours of calving.
3. In case ROP persists even after 12 hours of calving, tie a knot very close to the base and cut 2 inches below the knot and leave it. The knot will go in.
4. Do not try to remove the retained placenta by hand.
5. Feed one full tuber of radish once a week for four weeks.
Repeat breeding
 Application:
Application:
1. Start treatment on 1st or 2nd day of heat.
2. Feed orally in fresh form in the following order once a day along with jaggery and salt: (a)1 white radish daily for 5 days (b) 1 Aloe vera leaf daily for 4 days.(c) 4 handfuls of moringa leaves for 4 days. (d) 4 handfuls of cissus stem for 4 days. (e) 4 handfuls of curry leaves with turmeric for 4 days. (f) Repeat the treatment once again if the animal has not conceived.
Prolapse
Ingredients:
Aloe vera gel- from one full leaf; Turmeric powderone pinch; Mimosa pudica leaves- 2 handfuls.
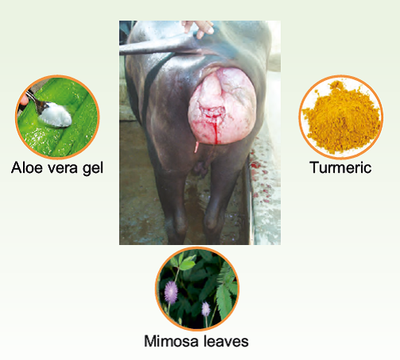 Preparation:
Preparation:
Remove the gel from a whole leaf.
Wash it multiple times till the sliminess is reduced.
Add a pinch of turmeric powder and boil to half the original volume and allow to cool
Prepare a paste of M. pudica leaves.
Application:
1. Clean the prolapsed mass
2. Sprinkle the gel on the prolapsed mass.
3. Apply M.pudica paste after the gel dries.
4. Repeat till the condition improves.
FMD mouth lesions
Ingredients:
Cumin seeds-10 g; Fenugreek seeds- 10 g; Black pepper- 10 g Turmeric powder – 10 g; Garlic- 4 pearls; Coconut- 1; Jaggery- 120 g.

Preparation:
1. Soak cumin, fenugreek and black pepper seeds in water for 20-30 mts.
2. Blend all ingredients to a fine paste.
3. Add 1 full grated coconut to the paste and mix by hand only.
4. Prepare dose freshly for each application.
Application:
1. Apply inside the mouth, tongue and palate.
2. Give the preparation thrice a day for 3 to 5 days.
FMD foot lesions/wound
Ingredients:
Acalypha indica leaves- 1 handful; Garlic-10 pearls; Neem leaves- 1 handful; Coconut or Sesame oil250ml; Turmeric powder – 20 g; Mehndi leaves- 1 handful; Tulsi leaves – 1 handful.
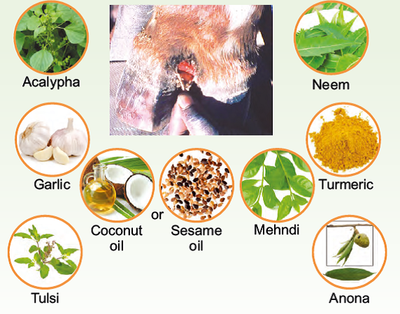
Preparation:
1. Blend all the ingredients thoroughly.
2. Mix with 250 ml coconut or sesame oil and boil and bring to cool.
Application:
1. Clean the wound and apply directly or bandage with a medicated cloth.
2. Apply Anona leaf paste or camphorated coconut oil for the first day only if maggots are present.
Fever
Ingredients:
Garlic– 2 pearls; Coriander- 10 g; Cumin-10 g; Tulsi1 handful; Dry cinnamon leaves-10 g; Black pepper10 g; Betel leaves- 5 no.s; Shallots- 2 bulbs; Turmeric powder- 10 g; Chirata leaf powder-20 g; Sweet basil- 1 handful; Neem leaves- 1 handful; Jaggery- 100 g.
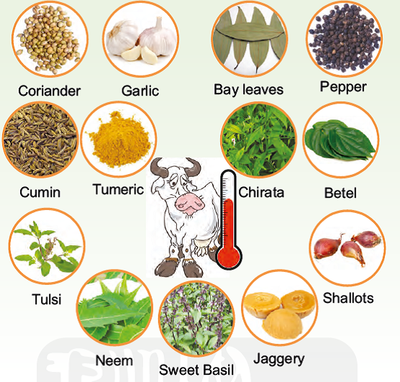
Preparation:
1. Soak cumin, pepper and coriander seeds in water for 15 mts.
2. Blend and mix all ingredients to form a paste.
Application:
1. Administer orally in small portions in the morning and evening.
Diarrhoea
Ingredients:
Fenugreek seeds – 10 g; Onion- 1 no.; Garlic- 1 pearl; Cumin seeds- 10 g; Turmeric- 10 g; Curry leaves- 1 handful; Poppy seeds – 5 g; Pepper- 10 g ; Jaggery- 100 g; Asafoetida- 5 g.

Preparation:
1. Dry fry cumin seeds, asafoetida, poppy seeds and fenugreek seeds till smoke emanates.
2. Cool and powder the fried seeds.
3. Blend it with rest of the ingredients to form a paste.
Application:
1. Roll the paste into small balls.
2. Administer orally in small portions once daily for 1-3 days till condition cures
Bloat and Indigestion
Ingredients:
Onion- 100 g; Garlic-10 pearls; Dry Chilly- 2; Cumin seeds- 10 g; Turmeric -10 g; Jaggery- 100 g; Pepper10 g; Betel leaves- 10 no.s; Ginger – 100 g.

Preparation:
1. Soak pepper and cumin seeds for 30 mts.
2. Blend along with other ingredients to form a paste.
Application:
1. Roll the paste into small balls.
2. Administer orally in small portions with salt 3-4 times a day for 3 days.
Worms
Ingredients:
Onion- 1 no; Garlic-5 pearls; Mustard seeds- 10 g; Neem leaves- 1 handful; Cumin- 10 g; Bitter gourd- 50 g; Turmeric- 5 g; Pepper- 5 g; Banana stem- 100 g; Common leucas -1 handful; Jaggery- 100 g.

Preparation:
1. Blend all the ingredients.
2. Add one litre of clean water.
3. Strain with a fine sieve or muslin cloth.
4. Transfer to a bottle attached to a sprayer.
Application:
1. Spray on the entire body of the animal.
2. Also spray on any cracks and crevices in the cattle shed.
3. Application can also be done using a cloth dipped in the solution.
4. Repeat once a week till the condition resolves.
5. Do the application only during sunny part of the day.
Tick/Ectoparasites
Ingredients:
Garlic– 10 pearls; Neem leaves- 1 handful; Neem fruit-1handful; Acorus rhizome- 10 g; Turmeric powder- 20 g; Lantana leaves- 1 handful; Tulsi leaves- 1 handful.

Preparation:
1. Soak pepper and cumin seeds for 30 mts.
2. Blend along with other ingredients to form a paste.
Application:
1. Roll the paste into small balls.
2. Administer orally in small portions with salt 3-4 times a day for 3 days.
Pox/wart/cracks
Ingredients:
Garlic-5 pearls; Turmeric powder- 10 g; Cumin seeds-15 g; Sweet basil – 1 handful; Neem leaves – 1 handful ; Butter(preferred) or ghee-50 g.
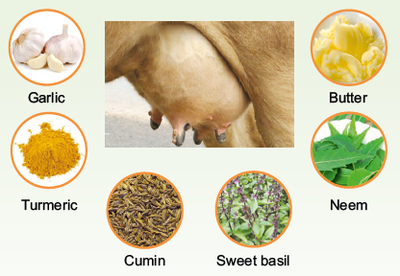
Preparation:
1. Soak cumin seeds in water for 15 mts.
2. Blend all ingredients to a fine paste.
3. Add butter and mix well.
Application:
1. Apply on affected part as many times as possible till condition resolves.
2. Apply after drying the skin surface.

INDIGENOUS TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE (ITK) PRACTICES IN LIVESTOCK FARMING IN INDIA
ITKs Used in Dysentery—–
• One hundred to one hundred fifty g stem, leaves of Anantamul (Indian sarsaparila, Hemidesmus indicus) is grounded and juice is extracted and mixed with honey and to be fed to the animal suffering from dysentery.
• Three pieces of Golmorich (Black pepper, Liquorice Glcyrrhiza glabra Piper nigrum), 2 teaspoon full ghee and 50 g smashed Jastimadhu are mixed with 250 ml cold water and to be drenched.
• One hundred ml sap is collected from the extract of Thankuni (Indian pennywort, Centella asiatica), Patharkuchi (Coleus aromaticus) and Durba(Dhub grass, Cynodon dactylon) and drenched to the cattle for 2-3 days.
• Fifty ml extract of Ganda (African marigold, Targetes erecta) shoot is mixed with 50 ml extract of Durba (Dhub grass, Cynodon dactylon) and is drenched to the animal.
• Three pieces of Golmorich (Black pepper, Piper nigrum), 5 g Jowan (Bishop’s weed, Trachyspermum ammi) and 5 g Chirata (Swertia angusti folia var pulchella) are grounded and fed to the animal for 3-4 days.
• One hundred g bark of Simul tree (Salmalia insignis, Bombax insigne) is boiled with 500 ml water and then being drenched to the animal.
• Latex of Chatim (Dita bark, Alstonia scholaris) is mixed with Golmorich (Black pepper, Piper nigrum) in the ratio of (3:2) to be given to animal.
• Bark of Palas tree (Butea monosperma) is boiled with 250 ml water and then is drenched to the cattle for 3-4 days.
• Two hundred g Kalmegh (Creat, Andrographis paniculata) leaves and 100 g Thankuni leaves (Indian pennywort, Centella asiatica) are grounded to make a paste and then fed to the cattle.
• One hundred ml extract of Kurchi (Holarrhena antidysenterica) leaves is drenched to the animal for 2-3 days.
• Decoction of the root of Babul (Acacia arabica) is mixed with mustard oil in the ratio of 1:3 and to be drenched to the animal.
ITKs Used in Arthritis———–
• Decoction of the root of Babul (Acacia arabica) is mixed with mustard oil in the ratio of 1:3 and to be drenched to the animal.
• Roots of Dhutra (Thorn apple, Jimson weed, Datura stramonium), Bonkul tree and Rasun (Garlic, Allium Sativum) are mixed and grounded. A paste is made and applied on the affected part.
• Hot fomentation is given with Akanda leaves (Asclepiadaceae, Calolropis gigantea) along with ghee.
• A luke worm paste is made from Rasun (Garlic, Allium sativum) and ghee and applied on the affected part.
• Sometimes some people put warm iron on the affected part.•
ITKs Used in Dog bite——
• Roots of Bonson tree are mixed with 21 pieces Golmorich (Black pepper, Piper nigrum) and the paste is fed to the animal.
ITKs Used in Cough and cold——–:
• One hundred g Tulsi leaves (Holy basil, Ocimum sanctum) and 100 g Basak leaves (Adhatoda vasica) are boiled with water. Then extracted juice is mixed with 1-teaspoon honey and fed to the animal.
• Three to four pieces of Tejpata (Indian cassia lignea, Cinnamomum tamala), 50 g Ada (Ginger, Zingiber officinale) and Aswatha (Ficus religiosa) leaves are mixed. Extract is made from the mixture and is drenched to the animal along with water.
• Efflorcence of Tulsi (Holy basil, Ocimum sanctum) and Basak (Adhatoda vasica) leaves are mixed and extract is taken and mixed with ghee, Ada(Ginger, Zingiber officinale) and molasses and fed to the cattle.
• Fifty ml Begna leave’s sap, 50 ml sap of Ada (Ginger) and 3 pieces of grounded Black pepper are mixed and fed to the cattle.
• A paste is made from ghee, Golmorich (Black pepper, Piper nigrum), Ada (Ginger, Zingiber officinale) and Rasun (garlic, Allium sativum). Then it is divided into 2 parts. One part is fed to the animal and other part is topically applied over head and neck.
ITKs Used in Anoestrus———
• Seven pieces of chicken egg per day is to be fed for seven days.
• Twelve pieces of Kala (Edible banana, Musa paradisiaca) along with 400 g sugar are to be fed for 2 days.
• One hundred g paste is made from Jaba (Chinese hibiscus, Hibiscus rosa sinensis) flower’s bud and old sugarcane (Saccharum sinense) jaggery, then to be fed for 15 days.
• One hundred g Asok (Ashoka, Saraca asoka) tree’s bark is grounded and fed to the cattle.
• Two hundred g bark of Asok tree (Ashoka, Saraca asoca) is to be boiled with 1 litre milk, then, every day it is to be drenched with water for 15-20 days.
• A mixture is made with the extract of bark of Aswatha (Ficus religiosa) and gruel and is to be fed for 10-15 days.
ITKs Used in Wound———
• Sap extracted from leaves and stem of Kesurta (Scirpus grossus) is mixed with Rasun (Garlic, Allium sativum) and to be applied topically.
• Halud (Turmeric, Curcuma domestica) is grounded and applied topically.
• Extract of Ganda (African marigold, Targetes erecta) leaves is applied topically.
• Jiyeti plant is to be burnt and ash of Jiyeti is then mixed with coconut oil and applied over it.
• Extract of Visalyakarani leaves is applied topically.
• Powder is made by grinding the seeds of Ata (Custard apple, Annona squamosa) and applied topically on the worm-infested wound.
• Paste is made from root, bark of Jam (Syzgium jambolanum) and applied topically on wound.
• Fruits of Khudikathi are to be grounded and mixed with coconut oil and applied topically.
• Roots of Kuchila (Snakewood, Strychnos nux-vomica) and roots of Surjamukhi (Common sunflower, Helianthus annuus) is mixed with Palas (Butea monosperma) petals and mustard oil and applied topically over the wound.
• Latex of Akanda (Asclepiadaceae, Calotropis gigantica) is applied topically.•
ITKs Used in Bloat———
• Fifty g Amlaki (Emblic myrobalan, Emblica officinalis), 50 g Haritaki (Chebulic myrobalan, Terminalia chebula) and 50 g Bahera (Terminalia bellirica) are mixed and fed to the animal daily once for 7 days.
• Ten g bark of Aswatha (Banyon, Fiscus benghalensis), 10 g Ada (Ginger, Zingiber officinale) and 10 g salt are mixed and fed to the animal daily once for 7 days.
• A mixture is made from flower of Tal tree (Palmyra palm, Borassus flabellifer), flower of Halud (Turmeric, Curcuma domestica), fruit of Lata tree, soot of kitchen room, bark of Sonari tree and bark of Banahata and then fed to the cattle.
• One hundred g mixture is made of salt, Pyaj, Bakhad, Ada (Ginger, Zingiber officinale), bark of Aswatha and honey and then fed to the cattle for 3-4 days.A mixture is made with Pat alu (one type of potato), Halud, Bel, Gad (one type of creeper), ghee, Rasun, bark of Aswatha and then fed to the cattle.
• A mixture is prepared from burnt tobacco (Nicotiana tobacum), burnt Bhutta (Maize, Zea mays) and cockroach faeces and applied on the belly.
• One hundred ml sap extracted from leaves of Kadam (Anthrocephalus cadamba) is drenched to the cattle for 2-3 days.
• Mixture of 250 g Somraj (Centrathierum anthelminticum) and 250 g Indrajan (Pala indigo plant, Wrightia tinctoria) is fed to the cattle.
• Twenty ml decoction of stem bark of Kadam (Anthocephalus chinensis) is given to the animal.
• A 250 g mixture is made from Bitlaban (Natrum mur bit), grounded sulphur, molasses, black pepper and glue and then fed to the cattle.
ITKs Used in Diarrhoea———
• Pulp of 100 g old ripened Tentul (Tamarind, Tamarindus indica) is fed to the animal for two to three days.
• Fifty ml sap of Peyara (Common guava, Psidium guajava) leaves is fed. It is efficient for goat especially.
• Valukchairi trees bark and roots of Lajjawati (sensitive plant, Mimosa pudica), Apang (Prickly chab flower, Achyranthes aspera) and Chakunda are to be mixed and grounded. Then 100 pieces Gol morich (Black pepper, Piper nigrum) and 2 teaspoons ghee are added to it. In case of calf, 40 pieces Black pepper are to be added. Then daily 100 g is to be fed.
• Bonkutti’s leave and Kirkichi tree’s roots are taken in an earthen pot and mixed with 2000 ml water. Then the mixture is boiled till it becomes 500 ml. Then 125 ml is to be fed to the cattle daily.
• One hundred and fifty gram Pelakacha’s fruit is collected and smoked and then fed to the cattle.
• Juice of Anarash (Pine apple, Ananus comosus) leaves is mixed with water and then is to be drenched 100 ml daily for 2-3 days.
• Neem (Margosa tree, Azadirachta indica) leaves and bark of Daka and bark of Daniaa are mixed and sap is extracted from the mixture and then 100 ml of it is drenched everyday for 3-4 days.
• Six pieces of Simul (Bombax insigne, Salmalia insignis) seeds are pulverised and mixed with 250 ml butter milk, then filtrate of this is taken and mixed with goat faeces and to be fed for 3-4 times.
• Rakta Kambal leaves (Indian red water lily, Nymphaea nouchali) are mixed with soda and then fed to the cattle, 50 ml daily for 2-3 days when it is suffering from bloody diarrhoea.
• Sap of 250 ml Kala (Edible banana, Musa paradisiaca) leaves and 100 ml sap of Bans leaves (Bamboo, Bambusa arundinacea rundinacea) are mixed with 250 g sugar and fed to the cattle for 2-3 days.
• Bark and fruits of Bahera tree (Belliric myrobalam, Terminalia bellirica) are pulverised and mixed with water then it is boiled and to be fed 50 ml everyday for 4-5 days.
• Fifty ml sap of Tentul (Tamarind, Tamarindus indica) leaves and Sonal leaves are mixed with Gol morich (Black pepper, Piper nigrum) and then given orally for 3-4 days.
• One hundred ml sap of Kurchi (Holarkhena antidysenterica) leaves is to be fed to the cattle for 2-3 days.
• Fifty ml Juice obtained from bark of Sal tree (Sal, shorea robusta) and then it is to be drenched.
• Fifty to sixty ml decoction of stem-bark of Khair (Cutch tree, Acacia Catechu) is given to the animal twice daily for 2-3 days.
