Organic Certification & Record Keeping
Back

What is Certification?
Organic certification system is a quality assurance initiative, intended to assure quality, prevent fraud and promote commerce, based on set of standards and ethics.
It is a process certification for producers of organic food and other organic plant products.
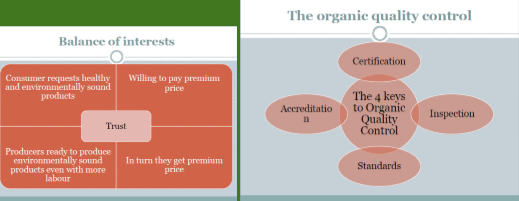
Accreditation:
As per the National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP) an accreditation refers registration by the accreditation agency for certifying agency for certifying organic farms, products and processes as per the guidelines of the National Accreditation Policy and Programme for Organic Product.
Guarantees that the certification program is competent to carry out specific tasks
Authoritative body defines policies, standards and checks whether a certification system is operating according to standards
Various accreditation programs: national, EU (EN45011), ISO (No. 65), IFOAM, NPOP, NOP, JAS
Function of accreditation agencies
In context of Indian accreditation scenario, NPOP defined the function of accreditation agencies like
Package of practices for organic products;
Accreditation of inspection and certifying agencies;
Monitor the inspection;
Lay down inspection procedures;
Advise the National Steering Committee
Accept Accredited certification programmes;
. Shall evolve accreditation criteria for inspection and/or certifying agencies;
. Shall prepare an operating manual to assist accredited agencies;
. Identification of Eligible inspection and certification agencies.
Standards:
Standards defining production methods, not the product quality
Minimum requirements, not “best practice”
Standards <--> regulations
Continuously developed, dynamic
Can be International, National or regional standards
Inspection
On-site visit to verify that the performance of an operation is in accordance with specific
standards
Evaluation and verification of agricultural production, processing and trading
Inspection requires complete documentation by producers, processors and handlers
Findings are presented in a report to the certifiers
Certification
Monitoring the market for misuse of certification mark or label
Assesses the results of the inspection in relation to the requirements of the organic standards
Decides about issuing of certificates, conditions and sanctions
Written confirmation that a process or product is in compliance with certain standards: Certificate is granted
Labelling
Easy recognition of organic quality and certification system
Confirms the fulfilment of the label regulations and of legal rules
They help to achieve a better price for organic products
NPOP has equivalence agreement with European Union
• NPOP has equivalence agreement with Switzerland
• USDA has accepted NPOP conformity assessment system
Means product certified by any Indian certification body can be exported without the need for recertification in above countries. For USA, Indian certification bodies issue certificate based on NOP standards

Inspection and Certification Process
Appointment of Inspection and Certification bodies
Accreditation of Inspection and certification agency by NAB
Deployment of competent persons for audit
Undertaking inspection and certification
Annual Surveillance and Review of Inspection and Certification Agencies
Continuous improvement in system
Renewal of accreditation at 3 year interval
Inspection and Certification by Accredited agency
Receipt of applications
Providing standards and operational documents
Agreement
Demand for Fee
Document audit
Physical field inspection
Risk assessment
Compliance verification
Reporting by inspector
Review by reviewer
Certification decision
Inspection methods
Visits of facilities, fields, farms etc.
Review of records and accounts.
Calculation of input/output norms, production estimates etc.
Assessment of production system
Interview with responsible persons
Risk assessment
Part Conversion and Parallel Production
Inspection for Use of Genetically Engineered Products
Use of off-farm inputs
Analysis for residue testing (if required)
Organic Dairy Farming: Organic Certification
Organic Certification process for Organic Dairy Farming
Organic Certification:
A written assurance is given by the Certification Agency that a clearly identified production or processing system has been methodically assessed and conforms to the specified requirements.
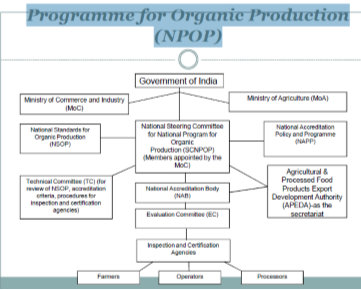
APEDA (Agriculture and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority) and NSOP (National Standards for Organic Products) are the important certifying agency. For Indian condition in case of small farmers, Group Certification is convenient as this step is investment intensive and there are 20 Accredited Certification Agencies (ISO-17011) in India.
1. During the registration of the dairy farm by the accredited Certification Body, the producer/farmer has to present an organic management plan which requires to be verified during the inspection.
How to get certified
Farmers must first register with an acknowledged inspection body or authority in their country and according to an agreed conversion plan they have to undergo a conversion period of a minimum of two years before they can begin producing dairy products that can be marketed as organic. During this time, the farm is said to be ‘in-conversion’.
If farmers wish to produce both conventional and organic products, these two operations must be clearly separate throughout every stage of production. They must be subject to inspections by acknowledged inspection bodies or authorities to ensure their compliance with organic legislation and the successful operators are then granted organic certification and are allowed to have their goods labeled as organic.
To certify a farm, the farmer is typically required to engage in a number of new activities, in addition to normal farming operations:
• Study the organic standards, which cover in specific information about what is and is not allowed for every aspect of farming, including storage, transport and sale.
• Farm facilities and production methods must comply with the standards, which may involve modifying facilities, sourcing and changing suppliers. • Extensive documentation is required, detailing farm history and current set-up, and usually including results of soil and water tests.
• Written annual production plan must be submitted, detailing everything from origin of animals to sale of milk, feed sources, farm locations, disease and parasite control activities, market locations, etc.
• Annual on-farm inspections are required, with a physical tour, examination of records, and an oral interview.
• Record keeping of day-to-day farming and marketing records, covering all activities, must be available for inspection at any time. In addition, short-notice or surprise inspections can be made, and specific tests (e.g. soil, water, plant tissue, milk test) may be requested.
2. To produce organic milk, dairy farm must be registered with an organic control body and production system
3. National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP) is a national body for promotion of organic farming.
The National Programme for Organic Production proposes to provide an institutional mechanism for the implementation of National Standards for Organic Production, through a National Accreditation Policy and Programme.
The aims of the National Programme for organic production are the following:
(a) To provide the means of evaluation of certification programmes for organic agriculture and products as per the approved criteria.
(b) To accredit certification programmes
(c) To facilitate certification of organic products in conformity to the National Standards for Organic Products.
(d) To encourage the development of organic farming and organic processing
4. There is recognition of Indian Organic Standards and certification system by EU and USA which provides a vast potential for export to these countries?
What does Organic Foods mean?
Organic foods are products of holistic agricultural practices focusing on bio-diversity, soil health, chemical free inputs etc. with an environmentally and socially responsible approach that have been produced in accordance with organic production standards.
People are wary to purchase organic food due to lack of confidence about its genuineness. The problem of fraud and mis-labelling occurs when a Food Business Operator (FBO) marks a product as organic while it contains non-organic ingredients or where the organic production standards are not adhered to in the production process. Therefore, it becomes important to check if the food labelled as “organic” is genuinely organic.
The Food Safety and Standards (Organic Foods) Regulations, 2017 are based on the standards of National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP) and Participatory Guarantee System (PGS-India).
How to get ‘India Organic’ Certification
India Organic Certification is a label given to organic products after validation, which ensures that the product or raw materials used in the product were grown through organic farming – without any chemical fertilizers, pesticides, or induced hormones.
A trademark – “India Organic” will be granted on the basis of compliance with the National Standards for Organic Production (NSOP). Communicating the genuineness as well as the origin of the product, this trademark is owned by the Government of India.
The National Standards for Organic Products was established in 2000 which ensures the authenticity of the organic product. The certification is issued by testing centers accredited by the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA), under the National Program for Organic Production of the Government of India.
Certifying Agency: APEDA
How to get Organic Certification label?——-
In order to get the label first, one need to book an organic certification agent and fill agent’s application form and put them in.
Now that the agent will review your application and decide whether your product stands as per the guidelines for authentication and are in compliance with NOP regulations and standards, the inspection of the site will be arranged by him.
What is the cost of this label? ——-
The total cost of this label will be calculated depending on application fee, site inspection fee and an annual certification fee which can be between 10,000-60,000 depending on the type of product, size of the production operation and the accredited agency one chooses
What is considered to get this certification? ——–
The farm or the product to get the certification needs to be associated with the authenticity since two to three years. For first time certification, the soil must meet the basic requirements of being free from the use of prohibited substances (synthetic chemicals, etc) for a number of years. A conventional farm must adhere to organic standards for this period then only it will fall under this category.
What’s the difference between USDA and ‘India organic’ certifications? —————–
The USDA label actually stands for the verification of the organic product in terms of their organic standards that describe the specific requirements that must be verified by USDA accredited agent before products can be labeled as USDA organic whereas ‘India organic’ is a label given to organic products after validation that ensures that the product or the raw materials used were grown through organic farming, without the use chemical fertilizers, pesticides, or induced hormones.
