 |
|
|
Translate this page in your preferred language:
|
| Parasitic Diseases: |
| Back |
Parasitic diseases:
The incidence of parasitic diseases varies greatly. Poorly fed animals suffer more, but optimum nutrition does not offer complete protection.
- Poor Nutrition - Trichostrongylosis is more in calves. Excellent nutrition but favorable environmental conditions favor Haemonchosis in calves.
- Specific nutritional deficiency such as cobalt, copper, phosphourus, or protein reduces animal resistance.
- Dung pat can act as reservoir for larvae, for 5 months in summer and 7-8 months in winter and when the outer covering softens by rain. Larvae come out.
Breaking up of dung pat and introduction of suitable dung beetles help in worm control.
- Feed contaminated with stools in the bran spreads infestation.
- Areas with severe winter and dry summer the load is low, but when winter is mild and summer is wet, serious outbreaks come up.
Specific signs include:
- The animal appears pale around the eyes (anaemia) has a dry, dull coat.
- Animal may appear to be swollen around the jaws owing to accumulation of body fluid (referred to as ‘bottle jaw’).
- In some cases, adult worms or tapeworm segments may be seen in the feces.
- Diarrhea (may be bloody), loss of weight, and death may occur.
Treating worms:
- If worm infestation is suspected all animals should treated with broad-spectrum dewormers (antihelmintics). For advice on which type of dewormer to use and the method of administration, one should consult a veterinarian.
Control Measures:
Control of parasites is a group treatment. Presence of one clinical case needs whole herd to be treated.
- Have balanced nutrition.
- If there is pasture, have rotational system for grazing.
- In housed animals, feed and water should not get contaminated with dung.
- Do not group young and old animals together.
- Give broad spectrum anthelmintics having 90% efficacy. Give medication twice per year for whole herd.
- Have timely diagnosis; by fecal examination.
- Examination of fecal samples of the herd, at regular intervals is necessary (in calves at the interval of 15 days, before and after monsoon, for 3 to 4 times in a year).
- The control measures mainly depend upon knowledge of live cycle of parasite in relation to climatic and biological factors.
|
PARASITIC DISEASES
Babesiosis : (Babesia bigemina)

Animal affected: Cattle, buffalo, exotic and crossbred cattle are the worst affected.
Symptoms/lesions:
- Fever, coffee coloured urine,
-
 Anaemia and jaundice. Anaemia and jaundice.
Treatment/Control:
- Blood examination is essential.
- Consult vety. doctor before any treatment is given.
- Trypan Blue (Ethicare) : 1-4 g slow i/v route
- Berenil : 0.8-1.6 g/100 kg B.W. i/m, Pronil - H ,0.5 ml./i/m.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Anaplasmosis : (A. marginale)

Animal affected: Mostly exotic & crossbred cattle.
Symptoms/lesions:
- Rise in temp., dyspnoea, increased pulse & respiration rate
- Suspended rumination, anaemia, constipation followed by diarrhoea,
- Mucous membranes become pale,
- Pregnant animal may abort,
- Animal may die.
Treatment/Control:
- Chlortetracycline 5-10 mg/kg 1/m.
- Tetracycline HCL 5 mg/kg
- Rolitetracycline HCL 4 mg/kg,
- Imidocorb 1-2 mg/kg i/m- 2 doses at 7 days interval.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Theileriosis: (Theileria annulata)

Animal affected: Exotic cattle, crossbred cattle with high percentage of exotic blood.
Symptoms/lesions:
- High fever,
- Enlargement of the superficial lymph glands,
- Lacrymation,
- Difficult respiration,
- Jaundice and anaemia.
Treatment/Control:
- Blood and lymph gland biopsy examination is essential.
- No specific treatmet is available.
- Long acting tetracycline alongwith blood transfusion given at early stage may help.
- Keep animals free of ticks by regular spraying of recommended insecticides.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Surra : (Trypanosoma evansi)
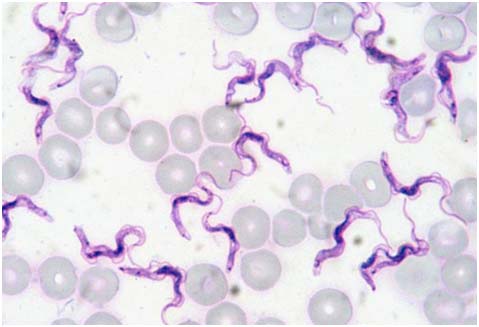
Animal affected: Horse, camel, cattle and buffalo
Symptoms/lesions:
- Fever,
- Nervous signs,
- Excitement, circling,
- Apparent blindness,
- Depression,
- Loss of body weight and anaemia.
Treatment/Control:
- Blood examination is essential.
- Gipol : 12 mg, per kg B.W. i/m,
- Berenil : 0.8-1.6 g/100 kg B.W. i/m,
- Tevansi, Inj : 5-10 ml. S/C,
- Tribexin Prosalt (3 g, vial) : Dissolve in 10 ml. dist. water, 1.3 ml. per 45 kg B.W. S/C.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ascariasis: (Toxocara vitulorum, Ascarisuum, Parascaris equorum, Toxocara canis and Ascaridia galli)
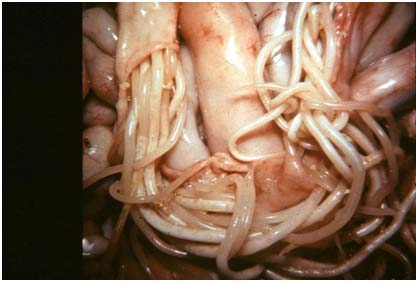
Animal affected: Buffalo/cow calf, young pig, horse dog, poultry.
Symptoms/lesions:
- Diarrhoea,
- Loss of body weight,
- Pendulous abdomen.
Treatment/:
- Faecal examination is essential.
- Lemasol powder : (20 g pouch) : 1-2 pouch per adult, cattle, 1 pouch per calf.
- Piperazine liquid (45%) : 30 ml/calf
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Liver Fluke Infection: (Fasciola gigantica)
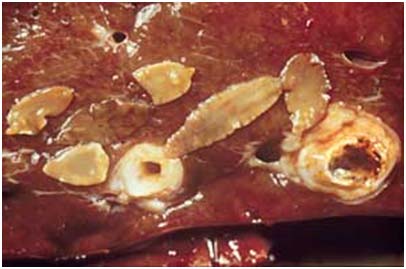 |
 |
| Mature Flukes in Liver
|
Egg of fasciola |
Animal affected: Sheep, goat, cattle & buffalo.

Symptoms/lesions:
- Diarrhoea,
- Emaciation,
- Oedema of the throat.
Treatment/Control:
- Faecal examination is essential
- Zanil 10-15 mg/kg B.W., orally.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Blook fluke infection: (Schistosoma spp.)
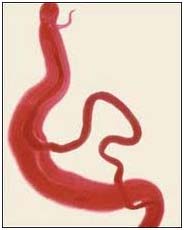
Animal affected: Buffalo and cattle
Symptoms/lesions:
- Loss of condition,
- Anaemia,
- Granulomatous growth inside nostrils.
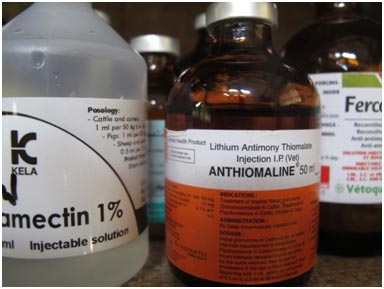
Treatment/Control:
- Consult a veterinary doctor.
- Anthiomaline (M&B) 20 ml, deep i/m twice a week is highly effective.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tapeworms Infection (Moniezia, Taenia, Echinococcus spp.)
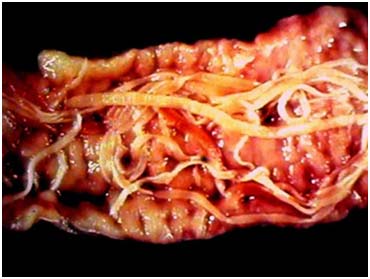
Animal affected: Sheep, goat, cattle & dog.
Symptoms/lesions:
- Vague abdominal trouble,
- Diarrhoea and constipation,
- Segments of the tape worm may be seen in the faeces.
Treatment/Control:
- Vague abdominal trouble,
- Diarrhoea and constipation,
- Segments of the tape worm may be seen in the faeces.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Mange (Sarcoptes scabiei, Psoroptes ovis, Demodex canis).
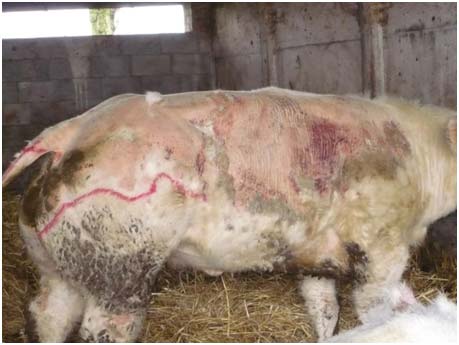
Animal affected: sheep and buffalo
Symptoms/lesions:
- Severe itching,
- Falling of hair,
- Scabs and crusts on affected skin,
- Occasionally pustules.
Treatment/Control:
- Skin scrapping examination is essential.
- Clip hair and scrub with warm water and soap.
- Apply 0.55 malathion or 0.15% lindane or
0.5% Sevin as spray, swab or dip, thrice at intervals of seven days.
- 1% Trichlorophon (Diptrex) ointement in vaseline,
- Ivermectin at the dose of 200 mg/kg B.W. is very effective.
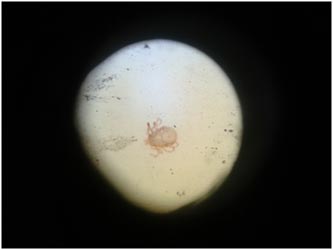
Some other Parasitic Diseases :
 |
 |
| Dicrocoelium |
Boophilus |
| |
|
 |
 |
| Rhipicephalus
|
Argas |


|
|
| Back |
|
|
Developed by :
|
Jaspal Singh
(Ex. M.V.Sc Scholar ) |
Dr. Pranav Kumar
(Assistant Professor)
|
Amandeep Singh
(Final Year B.V.Sc & AH student) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Scroll
|
Division of Veterinary and Animal Husbandry Extension Education
Faculty of Veterinary Sciences and Animal Husbandry, R.S. Pura, SKUAST Jammu |
|













 Anaemia and jaundice.
Anaemia and jaundice. 




