|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BROODING PROCESS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Back | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
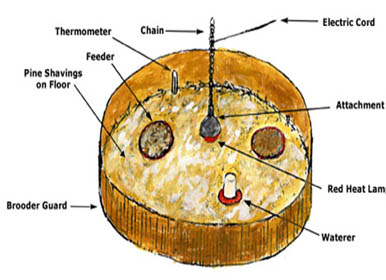
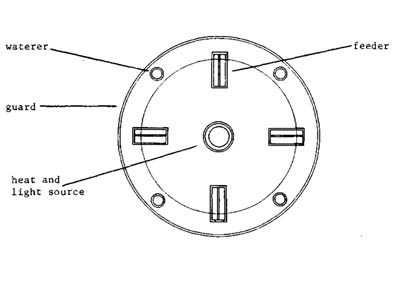
Materials required: Litter material, bulbs, thermometer, feeders, waterers, waste newspapers, lime powder, buckets, broomstick, electrolyte, etc.
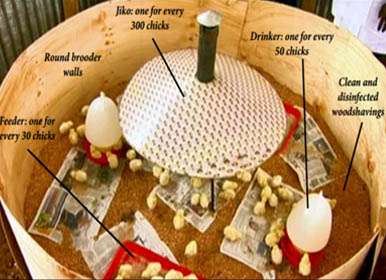
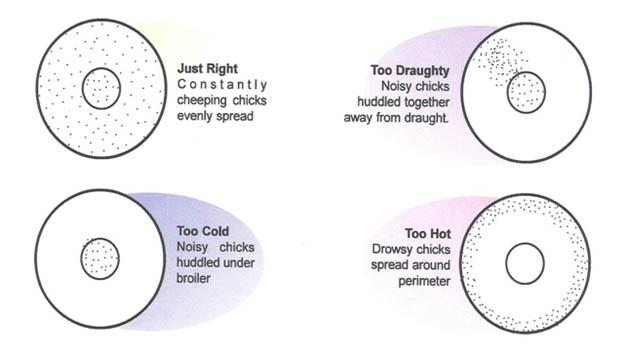
1. Remove spider webs, cobs, from the shed.. 2. Remove all the litter if brooding is carried in the previously built shed. 3. Wash shed with warm water. 4. Feeders and waterers should be thoroughly cleaned. Dry them in sun for a day. 5. The weight of the calf should be recorded. 6. Hang gunny bags around brooder house. The temperature should be maintained at 95 °F for 1st week and then reduce temperature 5°F on successive weeks for 4 weeks. 7. Spread the litter material upto a depth of 2 inches. 8. Place newspapers over the litter material 9. The feeders and waterers should be placed in a radiating manner from the light source. 10. 4 hours before the arrival of chicks, keep water in waterers to bring water at room temperature. 11. The brooding unit should be ready before a day prior on arrival of chicks. 12. The brooding bulb should be switched on at least 24 hours earlier to make the area warm at the time of housing the chicks. 13. Depending on weather conditions, put gunny bags around the brooding unit to maintain room temperature..
Time at which the successful brooding can be done without much intervention for the resources or climate suitable for brooding or time at which the chicks can be brought to house for rearing
Brooder Management: 1. Spread finely grained maize over the newspapers before arrival of chicks. 2. Give cool water after boiling. Add electrolyte and antibiotic (e.g. Enrofloxacin) for better results. 3. Distribute chicks equally under brooders. 4. Before putting chicks under brooder scale their beaks with water. 5. For first 3 days, give crushed maize twice a day. Subsequently add ground maize in small amounts.. 6. Change newspapers immediately if they get wet. 7. Remove newspapers on 5th day. 8.Remove wet litter immediately and add fresh litter. 9. According to the age, brooder temperature should be adjusted. 10. At 1st day, give glucose water, 5% glucose in liter of water. 11. 2nd to 4th day antibiotic i.e. Enrofloxacin and vitamin supplement i.e. Vimeral® should be given for better results in drinking water. 12.Wash the waterers daily and give fresh, cool water. 13.Give 24 hours light for 3 weeks to induce night feeding. 14. Chick mash should contain 23% crude protein and 2900 Kcal/kg of metabolizable energy.
Seasonal Modifications in Brooding Process: As far as the brooding in rural areas is concerned following modifications can be made as per the season 1. Bukharis can be used for brooding purposes.2. Lamps can be used in account for power cuts. 3. Feeding of maize, bran, grains, grams, kitchen waste, etc can be judiciously utilized as a feed source at par with the compound feed. However for proper growth of flock compound feed should be supplemented at times. 4. Give antibiotic, electrolyte, vitamin supplement for about a week. 5. Vaccination can be done if the area is prone to diseases, else the rearing can be carried out without the vaccines. 6. Market the chicks at an age of 28-30 days. 7. Restrict feed at 25 days for economizing the enterprise.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Back | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scroll | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Division of Veterinary and Animal Husbandry Extension Education Faculty of Veterinary Sciences and Animal Husbandry, R.S. Pura, SKUAST Jammu | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||